The Evolution of Digital Entrepreneurship: How AI & Innovation are Changing Startups
The Evolution of Digital Entrepreneurship
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, digital entrepreneurship has transformed from a niche option to the dominant paradigm for new ventures.
The intersection of technology, innovation, and entrepreneurial mindset has created unprecedented opportunities while simultaneously raising new challenges.
This comprehensive exploration tracks how entrepreneurship has evolved in the digital age, examines the impact of emerging technologies on business models, and provides insights into future trends that will shape the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
How Digital Transformation is Reshaping Business Models
The journey of entrepreneurship has undergone several fundamental shifts since the dawn of the internet era.
What began as simple e-commerce operations in the 1990s has blossomed into a complex ecosystem of digital platforms, software-as-a-service businesses, and technology-first ventures that would be unrecognizable to entrepreneurs of previous generations.
The Shifting Entrepreneurial Landscape
Traditional entrepreneurship often required substantial capital investment, physical locations, and extensive human resources before a business could serve its first customer.
The digital revolution has systematically dismantled these barriers. Today, a solo entrepreneur with a laptop, internet connection, and the right skills can launch a global business within days, sometimes with minimal upfront investment.
This democratization effect has several important implications:
- Expanded Accessibility: Entrepreneurship is no longer limited to those with access to significant financial resources or business connections.
- Accelerated Experimentation: Digital tools enable rapid prototyping, testing, and iteration of business ideas at a fraction of historical costs.
- Global Reach from Day One: Even the smallest startups can target and serve international markets immediately.
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: Cloud computing, SaaS tools, and digital workspaces have eliminated many fixed costs associated with business operations.
The result has been an explosion of innovation as more diverse founders with varied perspectives enter the entrepreneurial arena, bringing fresh solutions to both existing and emerging problems.
Online Business Models Driving the New Economy
The evolution of digital entrepreneurship has produced several distinctive business models that have come to dominate the startup landscape:
- Platform Businesses: Connecting producers and consumers through digital marketplaces (Uber, Airbnb, Etsy)
- Subscription Services: Providing ongoing value through regular payments (Netflix, Spotify, SaaS companies)
- Freemium Models: Offering basic services for free while charging for premium features (Dropbox, LinkedIn)
- Marketplace Models: Creating two-sided markets where the business facilitates transactions (Amazon, eBay)
- Creator Economy: Enabling individuals to monetize content, skills, and digital products (YouTubers, Substack writers)
- On-Demand Services: Delivering immediate solutions through technology (food delivery, remote consulting)
These models share common characteristics that distinguish them from traditional business approaches: they typically feature asset-light operations, prioritize scalability, leverage data as a competitive advantage, and focus on creating network effects to establish defensible market positions.
The Role of Technology in Digital Entrepreneurship Evolution
Technology isn’t merely a tool for entrepreneurs—it has become the primary catalyst for business innovation and the fundamental infrastructure upon which new ventures are built.
Disruptive Innovation in Entrepreneurship
Clayton Christensen’s concept of disruptive innovation has found its most fertile ground in the digital age. Tech-driven startups consistently demonstrate how small, agile teams can challenge established industry giants by:
- Targeting overlooked segments of the market
- Offering simpler, more accessible, or more affordable solutions
- Leveraging new technologies to solve problems in fundamentally different ways
- Creating entirely new markets that didn’t previously exist
Take the example of financial technology (fintech) startups that initially offered narrow services like peer-to-peer payments or automated investing to underserved segments.
Over time, these focused solutions expanded to challenge traditional banking services across the board, forcing established institutions to adapt or lose market share.
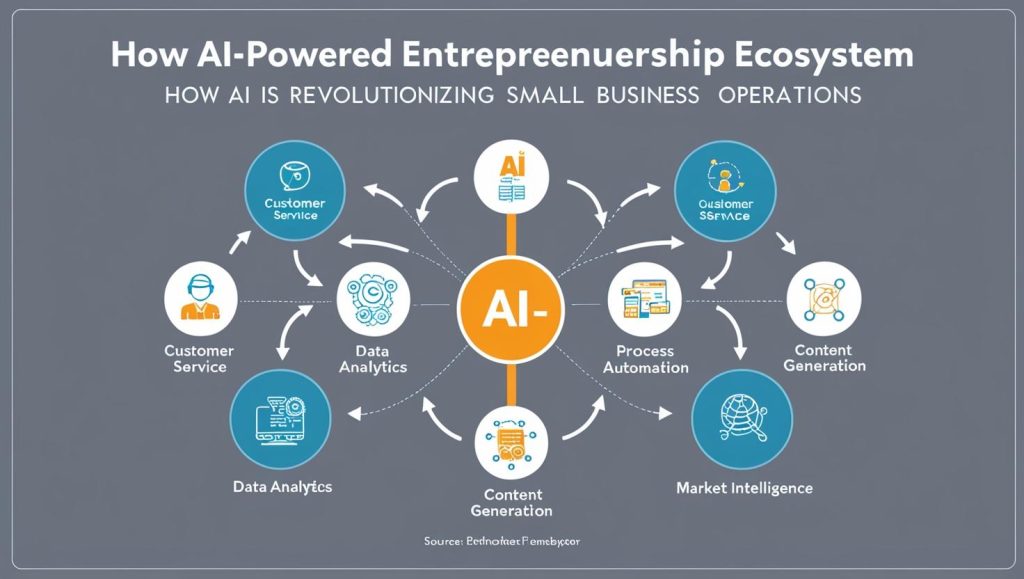
How AI is Revolutionizing Small Business Operations
Artificial intelligence has transitioned from cutting-edge technology to an essential component of digital entrepreneurship. Even small businesses now benefit from AI capabilities that were once available only to large corporations:
- Customer Service Automation: Chatbots and virtual assistants handle routine inquiries while routing complex issues to human representatives.
- Predictive Analytics: Small businesses can forecast trends, optimize inventory, and personalize marketing without large data science teams.
- Process Automation: Intelligent workflows reduce administrative burden and eliminate repetitive tasks.
- Content Generation: AI tools assist with creating marketing materials, product descriptions, and social media content.
- Market Intelligence: Advanced tools monitor competitors, track brand mentions, and identify emerging opportunities.
These applications democratize capabilities that would have required significant investment in the past, further leveling the playing field between startups and established businesses.
The Impact of Digital Transformation on Small Businesses
Digital transformation isn’t limited to new ventures—it’s reshaping existing small businesses across all sectors:
Traditional retailers now combine physical and digital experiences through omnichannel strategies. Local service businesses use digital tools to streamline scheduling, customer communication, and payment processing.
Manufacturing operations implement IoT sensors and data analytics to optimize production. Professional service providers deliver expertise through telemedicine, online consulting, and digital collaboration tools.
This evolution represents both opportunity and imperative. Small businesses that embrace digital transformation can expand their reach, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. Those that resist change face increasing competitive pressure as customer expectations evolve in alignment with digital capabilities.
The Entrepreneurial Mindset in the Digital Economy
While technology provides the tools, successful digital entrepreneurship still depends on human factors—particularly the entrepreneurial mindset that drives innovation and resilience.
Startup Success Factors in the Digital Age
Research into successful digital startups reveals several consistent patterns:
- Adaptability Over Planning: The most successful entrepreneurs demonstrate comfort with uncertainty and the ability to pivot based on market feedback.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Sustainable business models emerge from deep understanding of customer problems rather than attachment to specific solutions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Using metrics to guide strategy rather than relying solely on intuition or preference.
- Ecosystem Thinking: Building partnerships, integrations, and community connections that create value beyond the core offering.
- Continuous Learning: Commitment to ongoing skill development in response to rapidly evolving technologies and markets.
These factors highlight how the entrepreneurial mindset has evolved from the heroic, individualistic vision of the past to a more collaborative, experimental, and customer-focused approach.
The Lean Startup Model Applied
Eric Ries’s Lean Startup methodology has become foundational to digital entrepreneurship, emphasizing:
- Minimum Viable Products (MVPs): Creating the simplest version of a product that delivers value and generates learning.
- Build-Measure-Learn Cycles: Implementing rapid iteration based on actual customer feedback.
- Validated Learning: Testing assumptions through experiments rather than market research alone.
- Innovation Accounting: Developing meaningful metrics to evaluate progress in conditions of extreme uncertainty.
This approach has transformed how entrepreneurs develop products and business models, reducing wasted resources and increasing the probability of finding product-market fit before exhausting available capital.
Remote Work and Entrepreneurship: The New Normal
The acceleration of remote work arrangements has profound implications for digital entrepreneurship:
- Global Talent Access: Startups can build teams with specialized skills regardless of geographic location.
- Reduced Overhead: Office space requirements decrease or disappear entirely.
- Work-Life Integration: Entrepreneurs can structure work around personal priorities rather than traditional schedules.
- Distributed Teams: Organizations develop across multiple time zones, potentially enabling 24-hour productivity cycles.
- Location Independence: Founders can establish businesses from anywhere with reliable internet connectivity.
While remote work creates communication and culture challenges, it also expands entrepreneurial opportunities by removing geographic constraints and reducing initial costs.
Future Trends Shaping Digital Entrepreneurship
The evolution of entrepreneurship continues at an accelerating pace, with several emerging trends poised to reshape the landscape further.
AI-Powered Entrepreneurship Opportunities
Artificial intelligence is creating entirely new categories of entrepreneurial opportunity:
- Vertical AI Solutions: Specialized applications that solve industry-specific problems with unprecedented efficiency.
- AI-Enhanced Products: Traditional offerings improved through intelligent features and personalization.
- AI Infrastructure: Tools and platforms that make artificial intelligence capabilities accessible to non-specialists.
- Data Marketplaces: Ecosystems for sharing, acquiring, and monetizing the data that powers AI systems.
- AI Ethics and Governance: Services helping organizations navigate the complex ethical considerations of AI deployment.
For entrepreneurs, AI represents both a tool for internal efficiency and a source of product innovation that can create defensible competitive advantages.
Web3 and Blockchain-Based Business Models
Decentralized technologies are enabling novel business approaches that challenge conventional structures:
- Tokenized Economies: Creating new incentive systems through digital tokens that align user and platform interests.
- DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations): Organizations governed by smart contracts and community voting rather than traditional hierarchies.
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): Financial services provided through blockchain protocols without intermediaries.
- NFT-Based Businesses: Using non-fungible tokens to represent digital ownership, royalties, and access rights.
- Smart Contract Applications: Automating complex business arrangements through self-executing code.
These models remain experimental, but they suggest a future where entrepreneurship might operate with different foundational assumptions about ownership, governance, and value exchange.
Metaverse Business Opportunities on the Horizon
As virtual and augmented reality technologies mature, entrepreneurs are exploring commercial applications in immersive digital environments:
- Virtual Goods and Services: Creating and selling digital assets for use in virtual worlds.
- Experiential Commerce: Designing immersive shopping experiences that transcend physical limitations.
- Virtual Real Estate: Developing and monetizing digital locations within popular platforms.
- Extended Reality Training: Delivering educational and training content through immersive technologies.
- Virtual Events and Entertainment: Creating gatherings and performances in digital spaces.
While the full potential of the metaverse remains speculative, forward-thinking entrepreneurs are already establishing positions in what could become significant new markets.
Why Digital Entrepreneurs Fail and How to Succeed
Despite the opportunities, digital entrepreneurship continues to involve substantial risk, with important lessons emerging from both successes and failures.
Common Pitfalls in Tech-Driven Startups
Analysis of startup failures reveals several recurring challenges:
- Solution Without a Problem: Developing technology without validating market need or user demand.
- Premature Scaling: Expanding operations before establishing product-market fit.
- Ineffective Customer Acquisition: Unsustainable user growth strategies that consume capital without generating adequate returns.
- Technical Debt: Short-term development decisions that create long-term maintenance and scaling challenges.
- Team Misalignment: Founders with conflicting visions or complementary skills but incompatible working styles.
- Regulatory Oversights: Failing to anticipate legal and compliance requirements, particularly in regulated industries.
Understanding these common failure modes allows entrepreneurs to implement preventive measures and monitoring systems to identify problems early.
Sustainable Growth Strategies for Digital Businesses
Successful digital entrepreneurship increasingly emphasizes sustainability over growth at all costs:
- Unit Economics Focus: Ensuring profitability at the individual customer level before pursuing aggressive expansion.
- Balanced Funding Approach: Combining external investment with revenue generation rather than relying exclusively on venture capital.
- Operational Efficiency: Automating processes from the beginning to create scalable infrastructure.
- Strategic Partnerships: Leveraging existing platforms and ecosystems rather than building everything independently.
- Community Building: Developing engaged user communities that provide feedback, advocacy, and sometimes direct contributions.
These approaches reflect a maturing digital business environment where investors and entrepreneurs alike seek durable value creation rather than rapid exits.
Best Online Business Models for Beginners
For those entering digital entrepreneurship today, certain models offer more accessible entry points:
- Content Creation and Monetization: Building audiences through valuable content before introducing revenue streams like subscriptions, sponsorships, or digital products.
- E-commerce with Dropshipping: Selling products online without inventory management through fulfillment partnerships.
- Service Marketplaces: Connecting service providers with clients in specialized niches.
- Knowledge Products: Packaging expertise into courses, ebooks, or membership programs.
- Software Tools for Specific Verticals: Addressing overlooked problems in particular industries or professions.
These models typically feature lower initial investment requirements, clear paths to first revenue, and opportunities to grow organically through customer relationships.
The Impact of Technology on Digital Entrepreneurship Ecosystems
Beyond individual businesses, technology has transformed the broader environment in which entrepreneurship occurs.
Venture Capital in Digital Business
Investment in digital ventures has evolved significantly:
- Micro VC Firms: Smaller funds specializing in early-stage investments across specific sectors.
- Alternative Funding: Revenue-based financing, crowdfunding, and venture debt providing options beyond traditional equity.
- Accelerator Programs: Structured support combining capital, mentorship, and resources for early-stage companies.
- Corporate Venture Capital: Established companies investing in startups for strategic benefits beyond financial returns.
- Global Investment: Capital flowing across borders to find opportunities regardless of geography.
These developments have increased total funding availability while creating more specialized and sophisticated investment approaches tailored to different types of digital businesses.
Startup Incubators and Accelerators
Support structures for early-stage companies have proliferated and specialized:
- Vertical-Focused Programs: Accelerators targeting specific industries like healthcare, financial technology, or education.
- University-Affiliated Incubators: Academic institutions creating entrepreneurial ecosystems that leverage research and talent.
- Corporate Innovation Labs: Established companies creating environments for internal entrepreneurship and external collaboration.
- Remote Accelerators: Programs operating virtually to serve entrepreneurs regardless of location.
- Extended Engagement Models: Longer relationships between startups and supporting organizations beyond traditional demo days.
These structures provide entrepreneurs with resources, connections, and guidance that increase survival rates and accelerate development timelines.
No-Code Startup Trends Democratizing Tech
Perhaps the most significant recent development in digital entrepreneurship is the rise of no-code and low-code tools that enable non-technical founders to build sophisticated digital products:
- Visual App Builders: Platforms for creating mobile and web applications without programming expertise.
- Automated Workflows: Tools connecting various services to create complex business processes without custom integration code.
- Template Marketplaces: Pre-built solutions that can be customized for specific business needs.
- Visual Database Designers: Systems for creating and managing data structures through intuitive interfaces.
- AI-Assisted Development: Tools that generate code based on natural language descriptions of desired functionality.
These capabilities are redrawing the boundaries of who can participate in digital entrepreneurship, potentially unleashing innovation from individuals and communities previously excluded from technology creation.
Best Industries for Digital Entrepreneurship in 2025
Looking ahead, several sectors show particular promise for digital entrepreneurs:
- Healthcare Technology: Solutions addressing healthcare accessibility, preventive care, and administrative efficiency.
- Financial Wellness: Tools helping individuals and small businesses manage finances, build wealth, and access capital.
- Sustainability Solutions: Products and services supporting environmental goals and circular economy principles.
- Education Technology: Platforms reimagining learning experiences for different ages and contexts.
- Remote Work Infrastructure: Tools addressing persistent challenges in distributed work arrangements.
- Digital Wellness: Solutions balancing technological benefits with mental and physical health.
- Aging Population Services: Technologies supporting independence, health, and social connection for older adults.
These sectors combine significant market potential with meaningful impact opportunities, making them attractive for purpose-driven entrepreneurs.
The Future of Digital Entrepreneurship: Trends to Watch
As we look toward the horizon of digital entrepreneurship, several emerging patterns suggest how the field will continue to evolve.
AI Automation in Startups: Beyond Efficiency
The next wave of AI implementation will move beyond routine task automation to higher-level functions:
- Strategic Decision Support: AI systems providing scenario analysis and recommendation engines for business decisions.
- Creative Collaboration: Generative AI working alongside human teams in design, content, and product development.
- Autonomous Operations: Systems that can independently manage complex business processes with minimal oversight.
- Predictive Innovation: AI identifying unmet market needs and suggesting product directions before competitors.
These capabilities will further transform the entrepreneurial process, potentially changing the very nature of the founder’s role.
Crypto-Based Businesses: Beyond Speculation
As cryptocurrency markets mature, business models are emerging that leverage blockchain characteristics beyond financial speculation:
- Decentralized Identity: Solutions providing secure identity verification without centralized control.
- Transparent Supply Chains: Systems tracking product journeys with immutable records.
- Programmable Money: Financial services with behavior encoded directly into the currency itself.
- Tokenized Real-World Assets: Representing physical property, intellectual rights, and other tangible value in blockchain systems.
These approaches suggest how blockchain technology might move from alternative finance into mainstream business applications.
Sustainable Digital Entrepreneurship
Environmental and social considerations are becoming central to digital business strategy:
- Energy-Efficient Technology: Solutions designed to minimize computational resource requirements.
- Circular Economy Platforms: Digital marketplaces facilitating reuse, repair, and recycling.
- Impact Measurement Tools: Systems quantifying environmental and social outcomes alongside financial results.
- Inclusive Design Practices: Products developed with consideration for diverse user needs and accessibility requirements.
- Ethics-By-Design: Proactive approaches to potential harms embedded in product development processes.
These trends reflect both consumer demand and entrepreneur values, suggesting that future digital ventures will increasingly balance profit motives with broader impact considerations.
Conclusion: Embracing the Digital Entrepreneurial Evolution
The evolution of entrepreneurship in the digital age represents one of the most significant economic and social transformations in modern history. Technology has fundamentally altered who can become an entrepreneur, how businesses are built, what products and services can be created, and how value is delivered to customers.
For aspiring entrepreneurs, this evolution creates unprecedented opportunity—but also demands new skills, adaptability, and ethical consideration.
The most successful digital founders will combine technological leverage with human-centered approaches, building ventures that solve meaningful problems while navigating the complex challenges of our interconnected world.
The journey of entrepreneurship continues to evolve, but its essence remains: identifying opportunities, creating solutions, and delivering value in ways that improve people’s lives. In that fundamental purpose, digital entrepreneurship remains connected to its historical roots even as its methods, tools, and possibilities expand beyond what previous generations could have imagined.
FAQs About Digital Entrepreneurship
What is digital entrepreneurship?
Digital entrepreneurship involves creating, developing, and managing business ventures that leverage digital technologies as their primary means of operation, distribution, or value creation. Unlike traditional entrepreneurship, digital ventures typically feature asset-light models, rapid scalability, and technology-driven innovation.
How has digital transformation changed startups?
Digital transformation has lowered barriers to entry, accelerated development cycles, expanded market reach, and created entirely new business models for startups. It has shifted competitive advantage from physical resources toward data, network effects, and adaptation speed.
Why is entrepreneurship evolving in the digital age?
Entrepreneurship is evolving due to technological capabilities that reduce costs, increase experimentation opportunities, connect global markets, and automate complex processes. This evolution also responds to changing consumer expectations, workforce preferences, and social priorities.
What are the best online businesses to start?
The best online businesses align founder skills with market opportunities and personal interests. Currently promising models include specialized e-commerce, subscription services, digital products, remote services, content creation, and niche software solutions for underserved industries.
How can AI help small business owners?
AI helps small business owners by automating routine tasks, personalizing customer experiences, generating actionable insights from data, optimizing marketing spend, predicting business trends, and enabling capabilities previously available only to enterprises with significant resources.







